5 minutes, 22 seconds
-3.7K Views 0 Comments 0 Likes

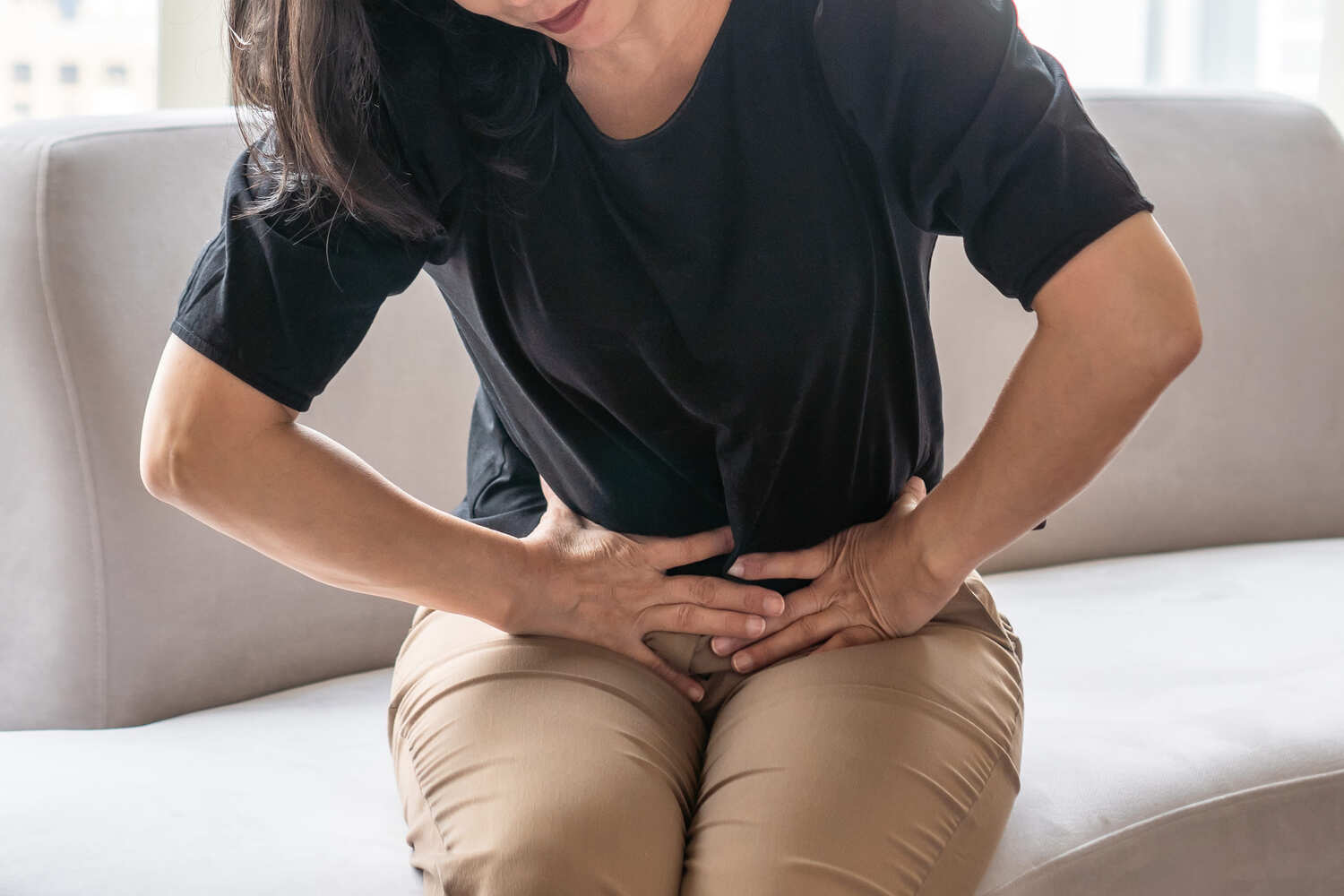
Uterine fibroids can produce painful and severe symptoms. Women seek help from their primary care physicians and gynecologists. Frequently, patients are informed that the only solution to relieve their discomfort and bleeding is to have the uterine fibroids removed through a hysterectomy.
However, this is not the only way a woman may treat fibroids. Fibroid therapy does not always require surgery. For almost 20 years, uterine fibroid embolization (UFE) has proven a safe and less invasive method of treating uterine fibroids.
UFE, also known as fibroid embolization, is an interventional radiology procedure that maintains a woman's uterus. Interventional radiology uses medical imaging technology to offer a variety of non-surgical therapies. Devices may include:
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI);
X-ray fluoroscopy;
Ultrasound;
Computed tomography.
Uterine fibroid embolization causes fibroids to shrink by cutting off their blood supply. The doctor makes a tiny puncture in the patient's wrist to gain access to the blood vessels. Using x-ray guidance, the doctor inserts a catheter into the blood vessels that supply the fibroid(s). Then they discharge little gelatin beads into the vessel(s), causing a blockage.
Patients may be alarmed when they hear the phrases "blood vessels" and "blockage" used together, as a blockage of vessels in the heart can cause serious, even fatal, damage. However, this restriction is not harmful. The doctor is merely cutting off the blood supply to the fibroid, not any other vital organs. When the blood flow is restricted, the fibroid begins to shrink, lowering or eliminating the patient's fibroid symptoms.
In addition to symptom alleviation, patients are satisfied with UFE since it:
Can boost fertility. Fibroids can affect a woman's ability to conceive. When she has a hysterectomy, she loses the ability to conceive. UFE therapy permits women to conceive naturally;
Does not have any harmful psychological effects.
Patients should consult their doctor before the surgery about any drugs or supplements they are taking, particularly pain relievers such as ibuprofen. Prior to treatment, their doctor may advise them to discontinue any blood thinners (including over-the-counter pain relievers and vitamin supplements) or drugs that might interfere with anesthesia.
On the day of therapy, the patient should bathe completely and avoid using lotions, deodorant, or perfume. Patients can expect to be sedated and anesthetized. As a result, patients must have a driver to transport them home following their surgery.
An IV will be used to provide relaxing medications. After the patient has relaxed, the doctor will administer a local anesthetic to numb the catheter injection site. The operation takes around an hour to complete.
The patient is then placed in a room to rest and wake up from the sedative. A nurse will continually assess the patient, and once they are comfortable and stable, they will be allowed to return home.
Most patients can resume their typical routines within two weeks. Sticking to a balanced diet and consuming enough water will help you recover quickly.
It will take between two and three months to detect an improvement in fibroid symptoms.
Patients will be given the following limitations by their doctor immediately following the treatment:
Shower as usual, but avoid baths;
Avoid using tampons during their next period;
Avoid sex, planes, and travel for two weeks;
Avoid hard lifting for a few weeks, or until they feel strong enough to handle it.
For the first week, avoid taking aspirin or any other blood thinners.
How does this relate to the healing period following a hysterectomy? Full recovery from a laparoscopic hysterectomy can take up to six weeks, with the first two weeks being the most painful and necessitating prescription pain relief. It might take up to 12 weeks for women to recover sufficiently to participate in sexual activity.