6 minutes, 7 seconds
-3.7K Views 0 Comments 0 Likes

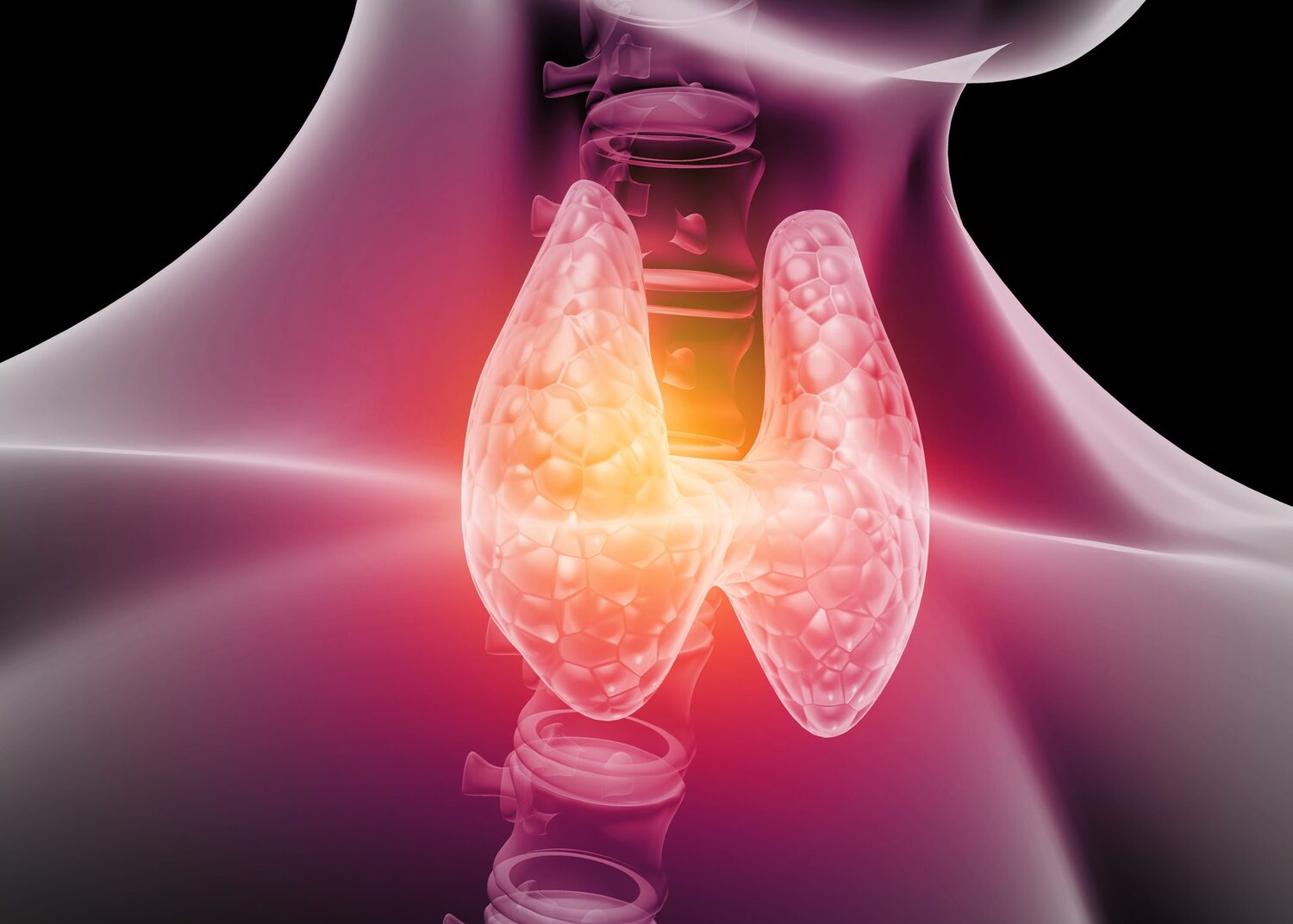
Thyroid diseases such as hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism are quite common and represent a serious health problem. The thyroid gland is an important organ in the endocrine system that regulates metabolism, heat exchange, growth, and development of the body. In this article, we will look at what hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism are, what the differences are, the causes and symptoms of each disease, as well as existing methods of diagnosis and treatment.
Hypothyroidism is a condition in which the thyroid gland doesn’t produce enough hormones. The thyroid gland releases two main hormones, thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3), which affect almost every tissue in the body. These hormones play a key role in metabolism, so a lack of production leads to a slowdown in metabolic processes.
Several causes can lead to hypothyroidism:
Autoimmune diseases. One of the most common causes of hypothyroidism is an autoimmune disease called Hashimoto's thyroiditis. In this disease, the immune system begins to attack the thyroid tissue and destroy the cells that produce hormones.
Iodine deficiency. Iodine is an important element necessary for the synthesis of thyroid hormones. In areas where dietary iodine levels are low, people can suffer from hypothyroidism if they don't get enough of this trace mineral.
Thyroid operations. Surgical removal of part or all of the thyroid gland due to various diseases, including cancer, can lead to hypothyroidism.
Treatment with radioactive iodine. This method of treating hyperthyroidism can lead to the development of hypothyroidism because radioactive iodine destroys thyroid cells.
Hypothyroidism develops slowly and its symptoms may not be noticeable for a long time. The main manifestations of hypothyroidism include:
Fatigue and weakness. A slowdown in metabolic processes in the body leads to constant fatigue.
Weight gain. Because their metabolism is slow, people with hypothyroidism often gain weight even when their diet remains the same.
Cold intolerance. People with hypothyroidism often feel cold even when the temperature is normal.
Dry skin and brittle hair. Lack of thyroid hormones affects the condition of the skin and hair.
Slow heart function. Patients may experience a slow pulse.
Concentration and memory problems. Thyroid hormones are important for the functioning of the nervous system, so their deficiency can lead to cognitive problems.
The main treatment for hypothyroidism is hormone therapy. An endocrinologist can prescribe medications that contain synthetic thyroid hormones, such as levothyroxine. This drug compensates for the lack of hormones and helps to normalize the metabolism. The dosage of the drug is selected individually and requires regular monitoring of hormone levels in the blood.
Hyperthyroidism is characterized by excessive activity of the thyroid gland and increased production of thyroid hormones. This condition leads to accelerated metabolism and can cause many serious problems in the body.
Hyperthyroidism can also occur for several reasons:
Graves' disease. In Graves' disease, the immune system produces antibodies that stimulate the thyroid gland, causing it to become overloaded.
Toxic nodular goiter. This condition occurs when nodules form in the thyroid gland and begin producing excess hormones.
Excessive iodine intake. Excessive iodine intake can lead to hyperthyroidism in some cases, especially if a person takes iodine supplements in high doses.
Viral infections. In rare cases, hyperthyroidism can develop in response to a viral infection that causes temporary inflammation of the thyroid gland.
The main symptoms of hyperthyroidism are associated with the acceleration of all metabolic processes in the body:
Weight loss. Even with normal or increased appetite, a person loses weight.
Feeling hot and excessive sweating. Patients often complain of a feeling of hotness, even when the ambient temperature is not high.
Hand tremors. The nervous system becomes too excitable, which can be manifested by shaking hands.
Rapid heart rate (tachycardia). An increase in heart rate is one of the characteristic signs of hyperthyroidism.
Nervousness and irritability. Psychoemotional disorders such as increased anxiety and nervousness often accompany hyperthyroidism.
Menstrual cycle disorders in women. Hormonal imbalance can lead to changes in the menstrual cycle.
There are several treatment options for hyperthyroidism. Medications that block the production of thyroid hormones (for example, thiamazole) help normalize hormone levels in the blood. Treatment with radioactive iodine destroys some thyroid cells, which leads to a decrease in hormone production. In some cases, partial or complete thyroid removal may be recommended to normalize hormone levels.