-
1,180 Views 0 Comments 0 Likes

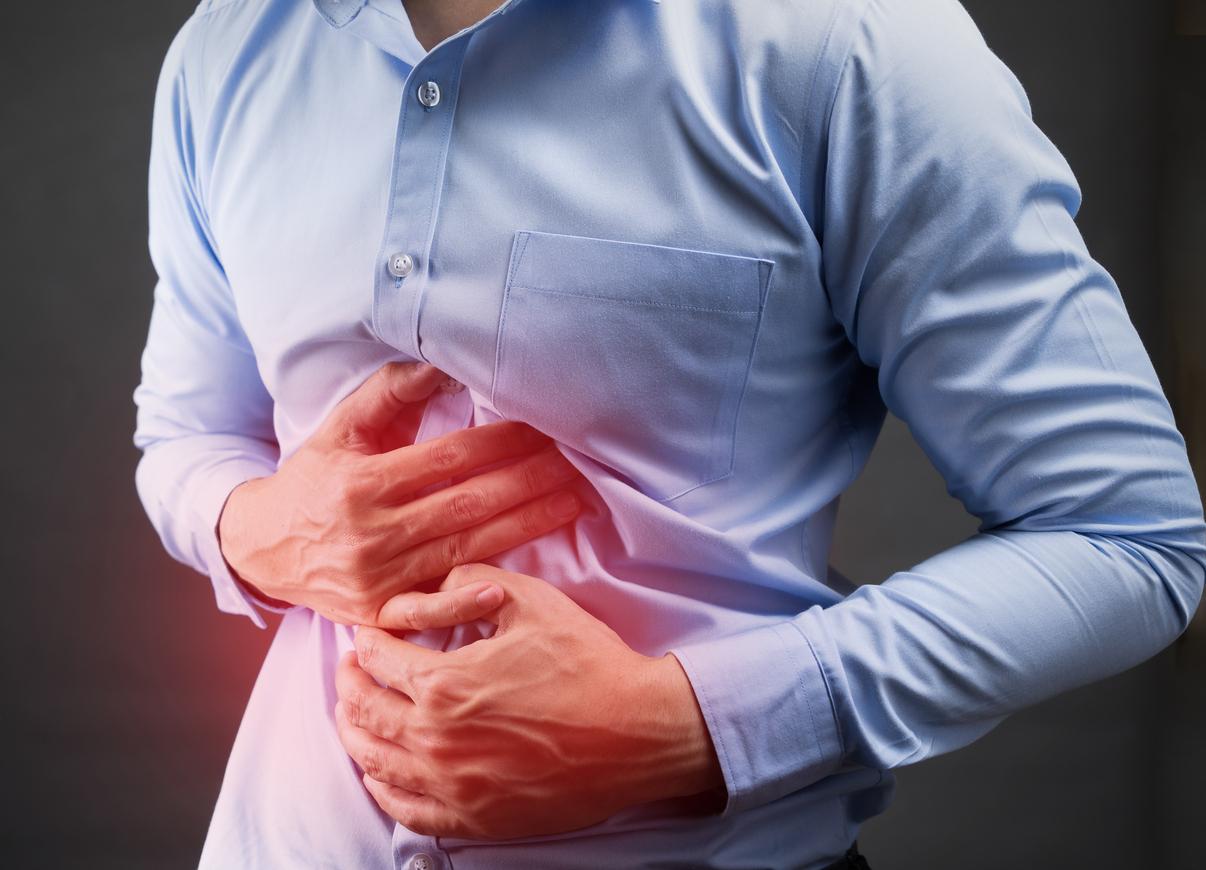
Upper abdominal pain can be caused by a variety of conditions, ranging from indigestion and heartburn to gallstones or a liver abscess. Most of the time, the pain is only temporary and goes away on its own. However, upper abdominal pain can be caused by something that necessitates immediate medical attention, such as a heart attack.
The lungs, heart, liver, gallbladder, and upper GI tract are all located in the upper abdomen. Knowing which organ or part of your body is affected can assist you and your doctor in determining the cause and type of treatment you require.
Indigestion, also known as dyspepsia, is a fairly common ailment. It causes stomach pain or bloating, heartburn, nausea, vomiting, feeling full early in a meal, feeling excessively full after eating, esophageal or stomach burning, and excessive gas.
Indigestion is usually caused by overeating, eating too quickly, or eating spicy, greasy, and fatty foods. It can also happen if you lie down soon after eating, which can make digestion more difficult.
Indigestion treatment options include lifestyle changes such as avoiding food triggers and limiting caffeine and alcohol consumption, as well as over-the-counter (OTC) or prescription medications such as antacids and stomach acid reduction medication.
GERD is a condition that occurs when stomach acid flows back into the esophagus. This causes irritation to the esophageal lining, which can result in symptoms such as heartburn, nausea, chest pain, vomiting, and coughing.
Heartburn is not a disease in and of itself, but rather a symptom of another. Heartburn is thought to be caused by health issues such as acid reflux and GERD.
Heartburn manifests as a burning sensation in the chest, usually behind the breastbone. The pain may spread to the throat and neck, and you may experience a bitter, sour taste in the back of your throat.
Blind loop syndrome occurs when food does not pass through the normal digestive route. It is caused by a massive overgrowth of bacteria in the intestines that forces food to go around it.
Blind loop syndrome is typically caused by complications following abdominal surgery, such as weight loss surgery. A peptic ulcer, Crohn's disease, or diverticulitis can also cause it.
Aside from abdominal pain, other symptoms of blind loop syndrome include fever, joint pain, a skin rash, and weight loss.
In some cases, the body will not receive all of the nutrients it requires. Antibiotics, corticosteroids to reduce inflammation, and corrective surgery are the standard treatments for blind loop syndrome.
Gallstones form when the digestive fluid in the gallbladder hardens. Gallstones range in size from a golf ball to a grain of sand and are composed primarily of cholesterol, calcium salts, bilirubin, and trace amounts of proteins.
Many people with gallstones have no symptoms, and the body will naturally expel them. If symptoms appear while the person has gallstones, they will almost certainly require surgery to remove them.
Cholecystitis is a condition characterized by gallbladder inflammation. It happens when bile gets stuck in the gallbladder. Gallstones, a bacterial infection, pancreatic or liver tumors, or a buildup of thick material in the gallbladder known as gallbladder sludge can all cause it.
A liver abscess is a pus-filled sac in the liver caused by bacteria, blood infection, liver damage, or an infection of the abdomen like appendicitis.
To treat a liver abscess, the abscess must be drained as well as antibiotics administered. If the spot is severe, surgery to remove it may be required.
Heart-Related Pain
A heart attack, also known as a myocardial infarction, is caused by a blocked artery. Medical attention is required immediately.
A heart attack is treated in a hospital with medications such as aspirin, antiplatelet agents, blood-thinning medications, nitroglycerin to improve blood flow, and ACE inhibitors to lower blood pressure.
Surgery may also be necessary. Coronary angioplasty and stenting and coronary artery bypass are two procedures that can be performed.
Pneumonia is an infection that causes inflammation of the lungs' air sacs. The air sacs may become clogged with liquid or pus, causing difficulty breathing and other symptoms.
Pneumonia frequently causes sharp or stabbing chest pain that worsens when a person coughs or breathes deeply.
The most common cause of pneumonia is bacteria, but it can also be caused by a viral infection. The cause of pneumonia will be treated.
A blood clot in the lungs is known as a pulmonary embolism. Because of restricted blood flow and a decrease in oxygen levels, the condition can be fatal and cause lung damage. Up to 30% of people who suffer from pulmonary embolism will die as a result of the condition.
Pulmonary embolism is usually treated in a hospital with blood-thinning medication, compression stockings, and sometimes surgery to improve blood flow and reduce the risk of future blood clots.
Upper abdominal pain can also be caused by physical trauma. Abdominal trauma can harm several internal organs, including the bowel, liver, intestines, and spleen.
Upper abdominal pain can be caused by blunt trauma to the upper body. Car accidents, assaults, falls, and various types of recreational accidents are all common causes of blunt trauma and abdominal injury.
Other symptoms of trauma will vary depending on the type of injury and other parts of the body that are affected. Trauma to the abdomen is thought to be one of the leading causes of death in young people worldwide.